|
ElasticSearch |
RDBMS |
|
Index |
表 |
|
Document |
行 |
|
Field |
列 |
|
Mapping |
表结构 |
在Elasticsearch 7.0版本之前(<7.0),有type的概念,而Elasticsearch和关系型数据库的关系是,index = database、type = table,但是在Elasticsearch 7.0版本后(>=7.0)弱化了type默认为_doc,而官方会在8.0之后会彻底移除type。
服务器选型
在官方文档(https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/heap-sizing.html)里建议Elasticsearch JVM Heap最大为32G,同时不超过服务器内存的一半,也就是说内存分别为128G和64G的服务器,JVM Heap最大只需要设置32G;而32G服务器,则建议JVM Heap最大16G,剩余的内存将会给到Filesystem Cache充分使用。如果不需要对分词字符串做聚合计算(例如,不需要 fielddata )可以考虑降低JVM Heap。JVM Heap越小,会导致Elasticsearch的GC频率更高,但Lucene就可以的使用更多的内存,这样性能就会更高。
对于我们公司的未来新增业务还会有收集用户的访问记录来统计PV(page view)、UV(user view),有一定的聚合计算,经过多方便的考虑与讨论,平衡成本与需求后选择了腾讯云的三台配置为CPU 16核、内存64G,SSD云硬盘的服务器,并给与Elasticsearch 配置JVM Heap = 32G。
需求场景选择
Elasticsearch在本公司系统的可使用场景非常多,但是作为第一次引入因慎重选择,给与开发与运维一定的时间熟悉与观察。
经过商讨,选择了两个业务场景,用户阅读作品的记录明细与作品搜索,选择这两个业务场景原因如下:
- 写场景
- 我们平台的用户黏度比较高,阅读作品是一个高频率的调用,因此用户阅读作品的记录明细可在短时间内造成海量数据的场景。(现一个月已达到了70G的数据量,共1亿1千万条)
- 读场景
- 阅读记录需提供给未来新增的抽奖业务使用,可从阅读章节数、阅读时长等进行搜索计算。
- 作品搜索原有实现是通过关系型数据库like查询,已是具有潜在的性能问题与资源消耗的业务场景
对于上述两个业务,用户阅读作品的记录明细与抽奖业务属于新增业务,对于在投入成本相对较少,也无需过多的需要兼容旧业务的压力。
而作品搜索业务属于优化改造,得保证兼容原有的用户搜索习惯前提下,新增拼音搜索。同时最好以扩展的方式,尽可能的减少代码修改范围,如果使用效果不好,随时可以回滚到旧的实现方式。
设计方案
共性设计
我使用.Net 5 WebApi将Elasticsearch封装成ES业务服务API,这样的做法主要用来隐藏技术细节(时区、分词器、类型转换等),暴露粗粒度的读写接口。这种做法在马丁福勒所著的《NoSQL精粹》称把数据库视为“应用程序数据库”,简单来说就是只能通过应用间接的访问存储,对于这个应用由一个团队负责维护开发,也只有这个团队才知道存储的结构。这样通过封装的API服务解耦了外部API服务与存储,调用方就无需过多关注存储的特性,像Mongodb与Elasticsearch这种无模式的存储,无需优先定义结构,换而言之就是对于存储已有结构可随意修改扩展,那么“应用程序数据库”的做法也避免了其他团队无意侵入的修改。
考虑到现在业务需求复杂度相对简单,MQ消费端也一起集成到ES业务服务,若后续MQ消费业务持续增多,再考虑把MQ消费业务抽离到一个(或多个的)消费端进程。
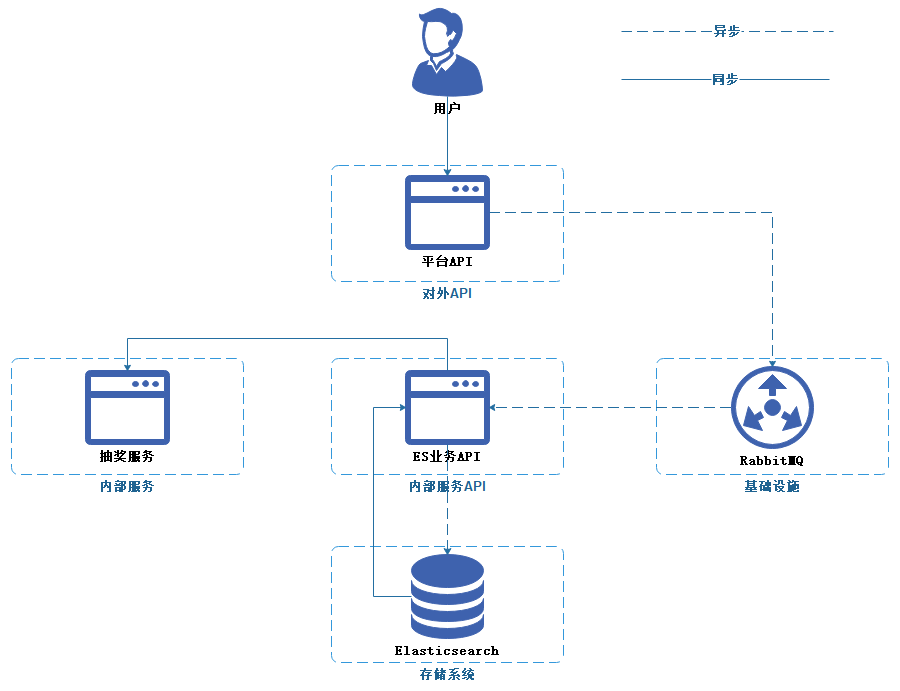
目前以同步读、同步写、异步写的三种交互方式,进行与其他服务通信。
阅读记录明细
本需求是完全新增,因此引入相对简单,只需要在【平台API】使用【RabbitMQ】进行解耦,使用异步方式写入Elasticsearch,使用队列除了用来解耦,还对此用来缓冲高并发写压力的情况。
对于后续新增的业务例如抽奖服务,则只需要通过RPC框架对接ES业务API,以同步读取的方式查询数据。
作品搜索
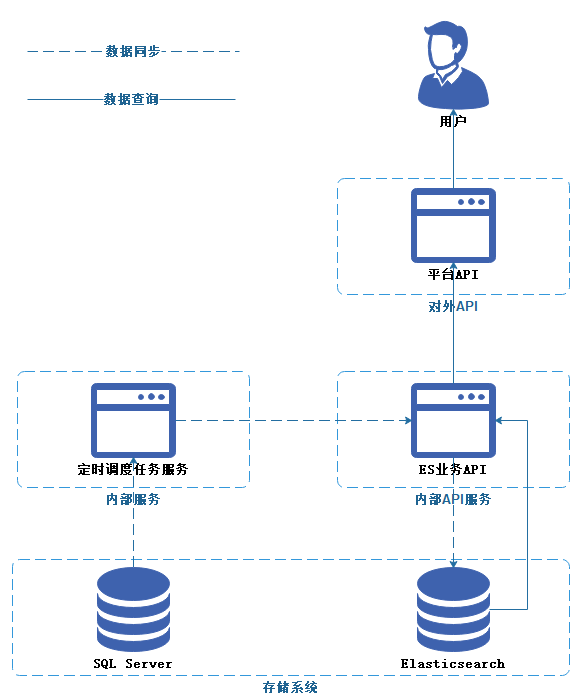
对于该业务,我第一反应采用CQRS的思想,原有的写入逻辑我无需过多的关注与了解,因此我只需要想办法把关系型数据库的数据同步到Elasticsearch,然后提供业务查询API替换原有平台API的数据源即可。
那么数据同步则一般都是分推和拉两种方式。
推
推的实时性无疑是比拉要高,只需增量的推送做写入的数据(增、删、改)即可,无论是从性能、资源利用、时效各方面来看都比拉更有效。
实施该方案,可以选择Debezium和SQL Server开启CDC功能。
Debezium由RedHat开源的,同时需要依赖于kafka的,一个将多种数据源实时变更数据捕获,形成数据流输出的开源工具,同类产品有Canal, DataBus, Maxwell。
CDC全称Change Data Capture,直接翻译过来为变更数据捕获,核心为监测服务捕获数据库的写操作(插入,更新,删除),将这些变更按发生的顺序完整记录下来。
我个人在我博客文章多次强调架构设计的输入核心为两点:满足需求与组织架构,在满足需求的前提应优先选择简单、合适的方案。技术选型应需要考虑自己的团队是否可以支撑。在上述无论是额外加入Debezium和kafka,还是需要针对SQL Server开启CDC都超出了我们运维所能承受的极限,引入新的中间件和技术是需要试错的,而试错是需要额外高的成本,在未知的情况下引入更多的未知,只会造成更大的成本和不可控。
拉
拉无疑是最简单最合适的实现方式,只需要使用调度任务服务,每隔段时间定时去从数据库拉取数据写入到Elasticsearch就可。
然而拉取数据,分全量同步与增量同步:
对于增量同步,只需要每次查询数据源Select * From Table_A Where RowVersion > LastUpdateVersion,则可以过滤出需要同步的数据。但是这个方式有点致命的缺点,数据源已被删除的数据是无法查询出来的,如果把Elasticsearch反向去跟SQL Server数据做对比又是一件比较愚蠢的方式,因此只能放弃该方式。
而全量同步,只要每次从SQL Server数据源全量新增到Elasticsearch,并替换旧的Elasticsearch的Index,因此该方案得全删全增。但是这里又引申出新的问题,如果先删后增,那么在删除后再新增的这段真空期怎么办?假如有5分钟的真空期是没有数据,用户就无法使用搜索功能。那么只能先增后删,先新增到一个Index_Temp,全量新增完后,把原有Index改名成Index_Delete,然后再把Index_Temp改成Index,最后把Index_Delete删除。这么一套操作下来,有没有觉得很繁琐很费劲?Elasticsearch有一个叫别名(Aliases)的功能,别名可以一对多的指向多个Index,也可以以原子性的进行别名指向Index的切换,具体实现可以看下文。
阅读记录实现细节
实体定义
优先定义了个抽象类ElasticsearchEntity进行复用,对于实体定义有三个注意的细节点:
1.对于ElasticsearchEntity我定义两个属性_id与Timestamp,Elasticsearch是无模式的(无需预定义结构),如果实体本身没有_id,写入到Elasticsearch会自动生成一个_id,为了后续的使用便捷性,我仍然自主定义了一个。
2.基于上述的分页深度的问题,因此在后续涉及的业务尽可能会以search_after+滚动加载的方式落实到我们的业务。原本我们只需要使用DateTime类型的字段用DateTime.Now记录后,再使用search_after后会自动把DateTime类型字段转换成毫秒级的Timestamp,但是我在实现demo的时候,去制造数据,在程序里以for循环new数据的时候,发现生成的速度会在微秒级之间,那么假设用毫秒级的Timestamp进行search_after过滤,同一个毫秒有4、5条数据,那么容易在使用滚动加载时候少加载了几条数据,这样就到导致数据返回不准确了。因此我扩展了个[DateTime.Now.DateTimeToTimestampOfMicrosecond()]生成微秒级的Timestamp,以此尽可能减少出现漏加载数据的情况。
3.对于Elasticsearch的操作实体的日期时间类型均以DateTimeOffset类型声明,因为Elasticsearch存储的是UTC时间,而且会因为Http请求的日期格式不同导致存放的日期时间也会有所偏差,为了避免日期问题使用DateTimeOffset类型是一种保险的做法。而对于WebAPI 接口或者MQ的Message接受的时间类型可以使用DateTime类型,DTO(传输对象)与DO(持久化对象)使用Mapster或者AutoMapper类似的对象映射工具进行转换即可(注意DateTimeOffset转DateTime得定义转换规则 [TypeAdapterConfig<DateTimeOffset, DateTime>.NewConfig().MapWith(dateTimeOffset => dateTimeOffset.LocalDateTime)])。
如此一来,把Elasticsearch操作细节隐藏在WebAPI里,以友好、简单的接口暴露给开发者使用,降低了开发者对技术细节认知负担。
[ElasticsearchType(RelationName = "user_view_duration")]
public class UserViewDuration : ElasticsearchEntity
{
/// <summary>
/// 作品ID
/// </summary>
[Number(NumberType.Long, Name = "entity_id")]
public long EntityId { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 作品类型
/// </summary>
[Number(NumberType.Long, Name = "entity_type")]
public long EntityType { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 章节ID
/// </summary>
[Number(NumberType.Long, Name = "charpter_id")]
public long CharpterId { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 用户ID
/// </summary>
[Number(NumberType.Long, Name = "user_id")]
public long UserId { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 创建时间
/// </summary>
[Date(Name = "create_datetime")]
public DateTimeOffset CreateDateTime { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 时长
/// </summary>
[Number(NumberType.Long, Name = "duration")]
public long Duration { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// IP
/// </summary>
[Ip(Name = "Ip")]
public string Ip { get; set; }
}
public abstract class ElasticsearchEntity
{
private Guid? _id;
public Guid Id
{
get
{
_id ??= Guid.NewGuid();
return _id.Value;
}
set => _id = value;
}
private long? _timestamp;
[Number(NumberType.Long, Name = "timestamp")]
public long Timestamp
{
get
{
_timestamp ??= DateTime.Now.DateTimeToTimestampOfMicrosecond();
return _timestamp.Value;
}
set => _timestamp = value;
}
}
异步写入
对于异步写入有两个细节点:
1.该数据从RabbtiMQ订阅消费写入到Elasticsearch,从下面代码可以看出,我刻意以月的维度建立Index,格式为 userviewrecord-2021-12,这么做的目的是为了方便管理Index和资源利用,有需要的情况下会删除旧的Index。
2.消息订阅与WebAPI暂时集成到同一个进程,这样做主要是开发、部署都方便,如果后续订阅多了,在把消息订阅相关的业务抽离到独立的进程。
按需演变,避免过度设计
订阅消费逻辑
public class UserViewDurationConsumer : BaseConsumer<UserViewDurationMessage>
{
private readonly ElasticClient _elasticClient;
public UserViewDurationConsumer(ElasticClient elasticClient)
{
_elasticClient = elasticClient;
}
public override void Excute(UserViewDurationMessage msg)
{
var document = msg.MapTo<Entity.UserViewDuration>();
var result = _elasticClient.Create(document, a => a.Index(typeof(Entity.UserViewDuration).GetRelationName() + "-" + msg.CreateDateTime.ToString("yyyy-MM"))).GetApiResult();
if (result.Failed)
LoggerHelper.WriteToFile(result.Message);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 订阅消费
/// </summary>
public static class ConsumerExtension
{
public static IApplicationBuilder UseSubscribe<T, TConsumer>(this IApplicationBuilder appBuilder, IHostApplicationLifetime lifetime) where T : EasyNetQEntity, new() where TConsumer : BaseConsumer<T>
{
var bus = appBuilder.ApplicationServices.GetRequiredService<IBus>();
var consumer = appBuilder.ApplicationServices.GetRequiredService<TConsumer>();
lifetime.ApplicationStarted.Register(() =>
{
bus.Subscribe<T>(msg => consumer.Excute(msg));
});
lifetime.ApplicationStopped.Register(() => bus?.Dispose());
return appBuilder;
}
}
订阅与注入
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
......
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env, IHostApplicationLifetime lifetime)
{
app.UseAllElasticApm(Configuration);
app.UseHealthChecks("/health");
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI(c =>
{
c.SwaggerEndpoint("/swagger/v1/swagger.json", "SF.ES.Api v1");
c.RoutePrefix = "";
});
app.UseRouting();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllers();
});
app.UseSubscribe<UserViewDurationMessage, UserViewDurationConsumer>(lifetime);
}
}
查询接口
查询接口此处有两个细节点:
1.如果不确定月份,则使用通配符查询userviewrecord-*,当然有需要的也可以使用别名处理。
2.因为Elasticsearch是记录UTC时间,因此时间查询得指定TimeZone。
[HttpGet]
[Route("record")]
public ApiResult<List<UserMarkRecordGetRecordResponse>> GetRecord([FromQuery] UserViewDurationRecordGetRequest request)
{
var dataList = new List<UserMarkRecordGetRecordResponse>();
string dateTime;
if (request.BeginDateTime.HasValue && request.EndDateTime.HasValue)
{
var month = request.EndDateTime.Value.DifferMonth(request.BeginDateTime.Value);
if(month <= 0 )
dateTime = request.BeginDateTime.Value.ToString("yyyy-MM");
else
dateTime = "*";
}
else
dateTime = "*";
var mustQuerys = new List<Func<QueryContainerDescriptor<UserViewDuration>, QueryContainer>>();
if (request.UserId.HasValue)
mustQuerys.Add(a => a.Term(t => t.Field(f => f.UserId).Value(request.UserId.Value)));
if (request.EntityType.HasValue)
mustQuerys.Add(a => a.Term(t => t.Field(f => f.EntityType).Value(request.EntityType)));
if (request.EntityId.HasValue)
mustQuerys.Add(a => a.Term(t => t.Field(f => f.EntityId).Value(request.EntityId.Value)));
if (request.CharpterId.HasValue)
mustQuerys.Add(a => a.Term(t => t.Field(f => f.CharpterId).Value(request.CharpterId.Value)));
if (request.BeginDateTime.HasValue)
mustQuerys.Add(a => a.DateRange(dr =>
dr.Field(f => f.CreateDateTime).GreaterThanOrEquals(request.BeginDateTime.Value).TimeZone(EsConst.TimeZone)));
if (request.EndDateTime.HasValue)
mustQuerys.Add(a =>
a.DateRange(dr => dr.Field(f => f.CreateDateTime).LessThanOrEquals(request.EndDateTime.Value).TimeZone(EsConst.TimeZone)));
var searchResult = _elasticClient.Search<UserViewDuration>(a =>
a.Index(typeof(UserViewDuration).GetRelationName() + "-" + dateTime)
.Size(request.Size)
.Query(q => q.Bool(b => b.Must(mustQuerys)))
.SearchAfterTimestamp(request.Timestamp)
.Sort(s => s.Field(f => f.Timestamp, SortOrder.Descending)));
var apiResult = searchResult.GetApiResult<UserViewDuration, List<UserMarkRecordGetRecordResponse>>();
if (apiResult.Success)
dataList.AddRange(apiResult.Data);
return ApiResult<List<UserMarkRecordGetRecordResponse>>.IsSuccess(dataList);
}
作品搜索实现细节
实体定义
SearchKey是原有SQL Server的数据,现需要同步到Elasticsearch,仍是继承抽象类ElasticsearchEntity实体定义,同时这里有三个细节点:
1. public string KeyName,我定义的是Text类型,在Elasticsearch使用Text类型才会分词。
2.在实体定义我没有给KeyName指定分词器,因为我会使用两个分词器:拼音和默认分词,而我会在批量写入数据创建Mapping时定义。
3.实体里的 public List<int> SysTagId 与SearchKey在SQL Server是两张不同的物理表,是一对多的关系,在代码表示如下,但是在关系型数据库是无法与之对应和体现的,这就是咱们所说的“阻抗失配”,但是能在以文档型存储系统(MongoDB、Elasticsearch)里很好的解决这个问题,可以以一个聚合的方式写入,避免多次查询关联。
[ElasticsearchType(RelationName = "search_key")]
public class SearchKey : ElasticsearchEntity
{
[Number(NumberType.Integer, Name = "key_id")]
public int KeyId { get; set; }
[Number(NumberType.Integer, Name = "entity_id")]
public int EntityId { get; set; }
[Number(NumberType.Integer, Name = "entity_type")]
public int EntityType { get; set; }
[Text(Name = "key_name")]
public string KeyName { get; set; }
[Number(NumberType.Integer, Name = "weight")]
public int Weight { get; set; }
[Boolean(Name = "is_subsidiary")]
public bool IsSubsidiary { get; set; }
[Date(Name = "active_date")]
public DateTimeOffset? ActiveDate { get; set; }
[Number(NumberType.Integer, Name = "sys_tag_id")]
public List<int> SysTagId { get; set; }
}
数据同步
数据同步我采用了Quartz.Net定时调度任务框架,因此时效不高,所以每4小时同步一次即可,有42W多的数据,分批进行同步,每次查询1000条数据同时进行一次批量写入。全量同步一次的时间大概2分钟。因此使用RPC调用[ES业务API服务]。
因为具体业务逻辑已经封装在[ES业务API服务],因此同步逻辑也相对简单,查询出SQL Server数据源、聚合整理、调用[ES业务API服务]的批量写入接口、重新绑定别名到新的Index。
[DisallowConcurrentExecution]
public class SearchKeySynchronousJob : BaseJob
{
public override void Execute()
{
var rm = SFNovelReadManager.Instance();
var maxId = 0;
var size = 1000;
string indexName = "";
while (true)
{
//避免一次性全部查询出来,每1000条一次写入。
var searchKey = sm.searchKey.GetList(size, maxId);
if (!searchKey.Any())
break;
var entityIds = searchKey.Select(a => a.EntityID).Distinct().ToList();
var sysTagRecord = rm.Novel.GetSysTagRecord(entityIds);
var items = searchKey.Select(a => new SearchKeyPostItem
{
Weight = a.Weight,
EntityType = a.EntityType,
EntityId = a.EntityID,
IsSubsidiary = a.IsSubsidiary ?? false,
KeyName = a.KeyName,
ActiveDate = a.ActiveDate,
SysTagId = sysTagRecord.Where(c => c.EntityID == a.EntityID).Select(c => c.SysTagID).ToList(),
KeyID = a.KeyID
}).ToList();
//以一个聚合写入到ES
var postResult = new SearchKeyPostRequest
{
IndexName = indexName,
Items = items
}.Excute();
if (postResult.Success)
{
indexName = (string)postResult.Data;
maxId = searchKey.Max(a => a.KeyID);
}
}
//别名从旧Index指向新的Index,最后删除旧Index
var renameResult = new SearchKeyRenameRequest
{
IndexName = indexName
}.Excute();
}
}
}
业务API接口
批量新增接口这里有2个细节点:
1.在第一次有数据进来的时候需要创建Mapping,因为得对KeyName字段定义分词器,其余字段都可以使用AutoMap即可。
2.新创建的Index名称是精确到秒的 SearchKey-202112261121
/// <summary>
/// 批量新增作品搜索列表(返回创建的indexName)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="request"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[HttpPost]
public ApiResult Post(SearchKeyPostRequest request)
{
if (!request.Items.Any())
return ApiResult.IsFailed("无传入数据");
var date = DateTime.Now;
var relationName = typeof(SearchKey).GetRelationName();
var indexName = request.IndexName.IsNullOrWhiteSpace() ? (relationName + "-" + date.ToString("yyyyMMddHHmmss")) : request.IndexName;
if (request.IndexName.IsNullOrWhiteSpace())
{
var createResult = _elasticClient.Indices.Create(indexName,
a =>
a.Map<SearchKey>(m => m.AutoMap().Properties(p =>
p.Custom(new TextProperty
{
Name = "key_name",
Analyzer = "standard",
Fields = new Properties(new Dictionary<PropertyName, IProperty>
{
{ new PropertyName("pinyin"),new TextProperty{ Analyzer = "pinyin"} },
{ new PropertyName("standard"),new TextProperty{ Analyzer = "standard"} }
})
}))));
if (!createResult.IsValid && request.IndexName.IsNullOrWhiteSpace())
return ApiResult.IsFailed("创建索引失败");
}
var document = request.Items.MapTo<List<SearchKey>>();
var result = _elasticClient.BulkAll(indexName, document);
return result ? ApiResult.IsSuccess(data: indexName) : ApiResult.IsFailed();
}
重新绑定别名接口这里有4个细节点:
1.别名使用searchkey,只会有一个Index[searchkey-yyyyMMddHHmmss]会跟searchkey绑定.
2.优先把已绑定的Index查询出来,方便解绑与删除。
3.别名绑定在Elasticsearch虽然是原子性的,但是不是数据一致性的,因此得先Add后Remove。
4.删除旧得Index免得占用过多资源。
/// <summary>
/// 重新绑定别名
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
[HttpPut]
public ApiResult Rename(SearchKeyRanameRequest request)
{
var aliasName = typeof(SearchKey).GetRelationName();
var getAliasResult = _elasticClient.Indices.GetAlias(aliasName);
//给新index指定别名
var bulkAliasRequest = new BulkAliasRequest
{
Actions = new List<IAliasAction>
{
new AliasAddDescriptor().Index(request.IndexName).Alias(aliasName)
}
};
//移除别名里旧的索引
if (getAliasResult.IsValid)
{
var indeNameList = getAliasResult.Indices.Keys;
foreach (var indexName in indeNameList)
{
bulkAliasRequest.Actions.Add(new AliasRemoveDescriptor().Index(indexName.Name).Alias(aliasName));
}
}
var result = _elasticClient.Indices.BulkAlias(bulkAliasRequest);
//删除旧的index
if (getAliasResult.IsValid)
{
var indeNameList = getAliasResult.Indices.Keys;
foreach (var indexName in indeNameList)
{
_elasticClient.Indices.Delete(indexName);
}
}
return result != null && result.ApiCall.Success ? ApiResult.IsSuccess() : ApiResult.IsFailed();
}
查询接口这里跟前面细节得差不多:
但是这里有一个得特别注意的点,可以看到这个查询接口同时使用了should和must,这里得设置minimumShouldMatch才能正常像SQL过滤。
should可以理解成SQL的Or,Must可以理解成SQL的And。
默认情况下minimumShouldMatch是等于0的,等于0的意思是,should不命中任何的数据仍然会返回must命中的数据,也就是你们可能想搜索(keyname.pinyin=’chengong‘ or keyname.standard=’chengong‘) and id > 0,但是es里没有存keyname=’chengong’的数据,会把id> 0 而且 keyname != ‘chengong’ 数据给查询出来。
因此我们得对minimumShouldMatch=1,就是should条件必须得任意命中一个才能返回结果。
在should和must混用的情况下必须得注意minimumShouldMatch的设置!!!
/// <summary>
/// 作品搜索列表
/// </summary>
/// <param name="request"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[HttpPost]
[Route("search")]
public ApiResult<List<SearchKeyGetResponse>> Get(SearchKeyGetRequest request)
{
var shouldQuerys = new List<Func<QueryContainerDescriptor<SearchKey>, QueryContainer>>();
int minimumShouldMatch = 0;
if (!request.KeyName.IsNullOrWhiteSpace())
{
shouldQuerys.Add(a => a.MatchPhrase(m => m.Field("key_name.pinyin").Query(request.KeyName)));
shouldQuerys.Add(a => a.MatchPhrase(m => m.Field("key_name.standard").Query(request.KeyName)));
minimumShouldMatch = 1;
}
var mustQuerys = new List<Func<QueryContainerDescriptor<SearchKey>, QueryContainer>>
{
a => a.Range(t => t.Field(f => f.Weight).GreaterThanOrEquals(0))
};
if (request.IsSubsidiary.HasValue)
mustQuerys.Add(a => a.Term(t => t.Field(f => f.IsSubsidiary).Value(request.IsSubsidiary.Value)));
if (request.SysTagIds != null && request.SysTagIds.Any())
mustQuerys.Add(a => a.Terms(t => t.Field(f => f.SysTagId).Terms(request.SysTagIds)));
if (request.EntityType.HasValue)
{
if (request.EntityType.Value == ESearchKey.EntityType.AllNovel)
{
mustQuerys.Add(a => a.Terms(t => t.Field(f => f.EntityType).Terms(ESearchKey.EntityType.Novel, ESearchKey.EntityType.ChatNovel, ESearchKey.EntityType.FanNovel)));
}
else
mustQuerys.Add(a => a.Term(t => t.Field(f => f.EntityType).Value((int)request.EntityType.Value)));
}
var sortDescriptor = new SortDescriptor<SearchKey>();
sortDescriptor = request.Sort == ESearchKey.Sort.Weight
? sortDescriptor.Field(f => f.Weight, SortOrder.Descending)
: sortDescriptor.Field(f => f.ActiveDate, SortOrder.Descending);
var searchResult = _elasticClient.Search<SearchKey>(a =>
a.Index(typeof(SearchKey).GetRelationName())
.From(request.Size * request.Page)
.Size(request.Size)
.Query(q => q.Bool(b => b.Should(shouldQuerys).Must(mustQuerys).MinimumShouldMatch(minimumShouldMatch)))
.Sort(s => sortDescriptor));
var apiResult = searchResult.GetApiResult<SearchKey, List<SearchKeyGetResponse>>();
if (apiResult.Success)
return apiResult;
return ApiResult<List<SearchKeyGetResponse>>.IsSuccess("空集合数据");
}
APM监控
虽然在上面我做了足够的实现准备,但是对于上生产后的实际使用效果我还是希望有一个直观的体现。我之前写了一篇文章《.Net微服务实战之可观测性》很好叙述了该种情况,有兴趣的可以移步去看看。
在之前公司做微服务的时候的APM选型我们使用了Skywalking,但是现在这家公司的运维没有接触过,但是对于Elastic Stack他相对比较熟悉,如同上文所说架构设计的输入核心为两点:满足需求与组织架构,秉着我的技术选型原则是基于团队架构,我们采用了Elastic APM + Kibana(7.4版本),如下图所示:

